This post provides the basic foundations of management.
Engineers learn to build, Scientists build to learn & Managers make sure they do it the the most efficient way.
And the only reason this is here-on this blog is because many people move to managerial positions & whatever you’re doing in life, whatever you’ve done – is essentially just management. This post answers the fundamental questions of management that help developing a foundation for higher management studies.
What is an Organization?
We start with a the organization. An organization is a set of people, people who work together to achieve some purpose. And these people work in a certain organizational structure. So, an organization has 3 essential components – Purpose, People & Structure.
Organizations usually use a mission statement to define their purpose. The people in the organization may be operatives – individuals who work under the supervision of others(the managers). So managers direct the activities of operatives.
What is Management?
Management is then, the process of directing operatives to achieve the organization’s purpose effectively & efficiently. Efficiency is doing the tasks right & Effectiveness is doing the right tasks.
What is the management process?
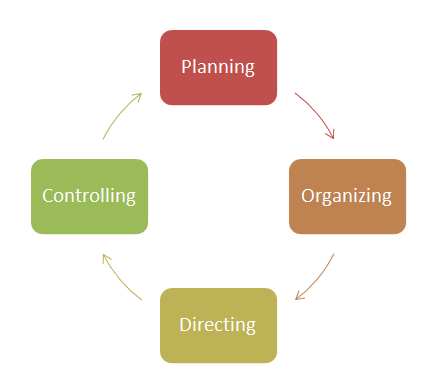
Essentially, there are 4 processes involved in management –
Planning(define goals & strategy), Organizing(define tasks/who does what), Leading or Directing(motive employees/resolve conflicts) & Controlling(monitor performance/compare with goals/correct deviations)
What roles does a manager play?
Now, all of us have heard of entrepreneurs, spokespersons, monitors, liaisons, and so on. These are all different roles played by managers. Henry Mintzberg classified 10 managerial roles as –
Interpersonal (figurehead, leader, liaison), Informational (monitor, disseminator, spokesperson) & Decisional(entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator) Roles.

(Steve Jobs – The most admired entrepreneur amongst teenagers | Image By matt buchanan [CC-BY-2.0])
What skills must a manager have?
There are also a certain set of skills that a manager must have – the ability to understand, work with & motivate others (Interpersonal), to coordinate the organization’s activities (Conceptual), to use tools & techniques of the field (Technical) & to build the right connections (Political).
What is Organizational Culture?
Just like sects, religious groups & tribes, the organization has certain rituals, traditions, languages, material symbols, etc that compose its culture. The culture determine, to a large degree, how the employees act. It is set up by the founders of the organization and the experiences of the first employees. A strong organizational culture overrides the structure(formal guidelines) of the organization.
‘Formal’ refers to anything which is written down/anything on paper while informal is not written down but is a result of common understanding/shared meaning.
What is Planning? What are the types of plans?
Planning involves defining goals, establishing a strategy to achieve these goals. Plans can be classified based on –
Breadth Of Use – Strategic (organization-wide; establish overall objectives) Vs Tactical (specific details on how to achieve these objectives)
Time Frame – Long Term (> one year) Vs Short Term (< one year)
Specificity – Directional (flexible ; only general guidelines) Vs Specific (clearly defined objectives ; no room for misinterpretation)
Frequency Of Use – Single Use (for a particular situation) Vs Standing (for repeatedly performed actions)
What is Controlling? What are the types of control?
In the management process, planning & control and complimentary components. Planning defines goals & Control checks if goals have been attained. Control itself involves 3 processes –
MEASURE – the actual performance is measured using personal observation(MBWA – management by walking around), statistical, written & oral reports.
COMPARE – this measured performance is then compared to a set standard. if variation is greater than a predefined accepted range of variation, it has to be corrected.
CORRECT – any deviations observed by comparing are then corrected. Corrective Action can be Immediate (to get performance back on track immediately) or Basic(correct the source of deviation to prevent further errors)
Also, There are 3 types/approaches of control –
Feedforward Control – Anticipates problems to correct them, Concurrent Control – Correct errors as they occur & Feedback Control – correct errors after they occur.
Managers have to deal with people. They must know how people think, what makes them happy & how they see the world in order to understand them & direct their work & behavior.
How managers predict an individuals personality?
Personality traits of a person can help managers predict their work-related behavior. Models used to predict personality are-
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator – classifies people into 16 personality types; determined by their answers to a set of 100 questions. [You can find your type at – http://www.humanmetrics.com/cgi-win/JTypes2.asp]
The Big 5 Model – Classifies personalities into 5 major categories based on – Extroversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Emotional Stability & Openness to Experience.
Personalities can then be matched to suitable jobs using Holland’s Topology. [You can take the Holland’s test at – http://www.soicc.state.nc.us/SOICC/planning/c1a.htm or http://www.roguecc.edu/counseling/hollandcodes/test.asp]
How do managers predict an individual’s perspective?
People do not see the reality(not yours, but theirs) – but a perception – their own image of the reality.
To judge a person’s perspective, we use –
The Attribution Theory – Judge people depending on their behavior & decide if the behavior is caused internally or externally. However, a fundamental attribution error exists – people believe that their own success is caused by internal factors while their failures are caused by external factors.
How do managers affect people’s learning?
Any change in the behavior of an individual is a consequence of what they have learned. When managers know how people learn, they can decide what they learn, and thus change their work-related behavior.
Managers provide positive and negative reinforcements to make people repeat or not repeat certain kinds of behavior.









